What is object storage?
Object storage is a method of data storage that emerged in the mid-1990s as researchers foresaw that existing storage methods would eventually start to show their limitations in certain scenarios. True to its name, object storage treats data as discrete units, or objects, that are accompanied by metadata and a universally unique identifier (UUID). This unstructured data resides in a flat (as opposed to tiered) address space called a storage pool. Object storage is also known for its compatibility with cloud computing, due to its unlimited scalability and faster data retrieval.
Today, as data comes to underpin everything we do, the adoption of object storage systems has increased. It’s common in data centers and popular cloud-based platforms, such as Google cloud storage or Amazon cloud storage, and has become the de facto standard in several enterprise use cases.
Object storage use cases
Server backup is one such use case. Cloud object storage is ideal for transferring large amounts of files offsite and storing them as unstructured data on a remote, cloud-hosted server. Along these same lines, cloud object storage is used in disaster recovery strategies to ensure the resilience and accessibility of backups.
Another use case falls under the umbrella of Big Data—fields like artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things and genomics. These all entail gathering massive amounts of unstructured data on an ongoing basis for later processing. Object storage is best suited to handle the volume and variety of this data.
Object storage vs. file storage
To best understand object storage, it helps to understand the ways it’s unlike file storage, which is the conventional data-storage method that everyday computer users are familiar with.
One popular analogy conceives of file storage as something like a library archive or a warehouse. All the data it contains is arranged hierarchically as folders within drawers within cabinets on shelves. Object storage, on the other hand, is like cars in an infinite number of gigantic parking lots. Each of those cars has a unique name (the UUID), and a valet will retrieve the right car based on the name you give them.
If you were to have an “object storage vs. file storage” showdown, each would bring different strengths:
Benefits of object storage
- Scalability: Because object storage isn’t concerned with things like partitions and trees, there’s no limit to the amount of data that can be stored. It can move seamlessly to the petabyte scale by just adding new nodes.
- Speed: Data retrieval with object storage is faster. As you’re dealing with chunks of unstructured data on an individual basis, there is no directory system to create a bottleneck.
- Lower cost: Cloud object storage is typically far less expensive than trying to expand traditional file systems or add new ones.
- Ease of use: The rich, customizable metadata that is an integral part of object storage makes it easier to analyze and work with stored data.
Benefits of file storage
- Compatibility: Given file storage’s long history in computing, it’s more likely to work with your existing applications and standard operating systems. Furthermore, without additional software, something like S3 object storage can’t be mounted and read like a USB drive.
- File locking: The basic mechanics of cloud object storage don’t allow shared files to be locked during editing. File storage, by contrast, “freezes” a shared file in a read-only mode during editing to prevent corruption.
- Granular permissions: By their very nature, hierarchical systems make it possible to assign different levels of access according to their different tiers.
- Random access: Modern file storage solutions permit you to read or write information anywhere in the file, whereas changed objects have to be rewritten to the store in their entirety.
How can you move data between object storage and file storage?
For these reasons, many organizations take a hybrid approach to data storage. They’ll use AWS object storage for large-scale data backups, for instance, and a NAS for commonly accessible local files. But how can you work with the unstructured data of object storage alongside the hierarchical data of file storage?
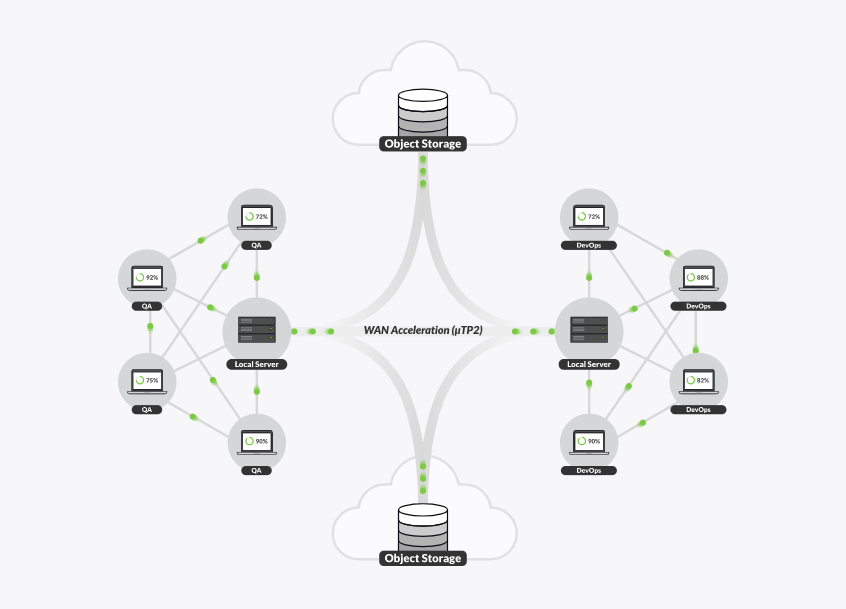
Resilio Connect is a fast and efficient way to transfer data to and from object storage and file storage, whether it’s in the cloud or on-premise. Its distributed peer-to-peer architecture can scale effortlessly to sync vast amounts of mission-critical data quickly between local storage and the cloud or even between cloud instances. Resilio Platform is fully compatible with AWS/S3 object storage, blob/Azure object storage as well as other major cloud providers, including Google cloud storage. In the object storage vs. file storage debate, the flexibility of Resilio Platform means you don’t have to choose a side.
For more information about how Resilio Platform can transfer data to and from object storage and file storage, please schedule a demo or start a free trial to find out.





